A budgie, also known as budgerigar or a common parakeet, is a small bird that belongs to the parrot family and is native to Australia. There are two common types of budgies, including the American (parakeet) and the English budgie. However, there is only one species of budgie, called the budgerigar but available in many color mutations.
But guess what? Like other animals, budgies are also prone to various health issues like respiratory infections, liver disease, and bacterial and viral infections. However, understanding liver disease in these birds is very important because it is one of the common health problems that affect them.
Also, understanding the illness may help with early detection. Even better, you get to know the various factors that contribute to the disease. Consequently, this allows you to minimize the risk of your bird contracting the disease. So then, what is budgie liver disease? Also, what are Budgie’s liver disease symptoms and treatment options?
As the name suggests, liver disease is a condition that affects a parakeet’s liver function. It can be in the form of inflammation or infection. Symptoms of this disease include reduced appetite, weight loss, lethargy, jaundice, diarrhea, and irritability. On the other hand, treatment options available are dietary changes, medication, and supportive care.
But what are the causes of this disorder? This guide covers everything there is to know about the anatomy of budgie liver, diagnosis methods, and preventive tips.
1. The Anatomy and Function of the Budgie Liver
The liver is an essential part of the budgie’s organ system, located in the abdominal cavity, behind the lungs, and the heart. Typically, this organ is dark or reddish brown but may turn yellow during the hatching period.
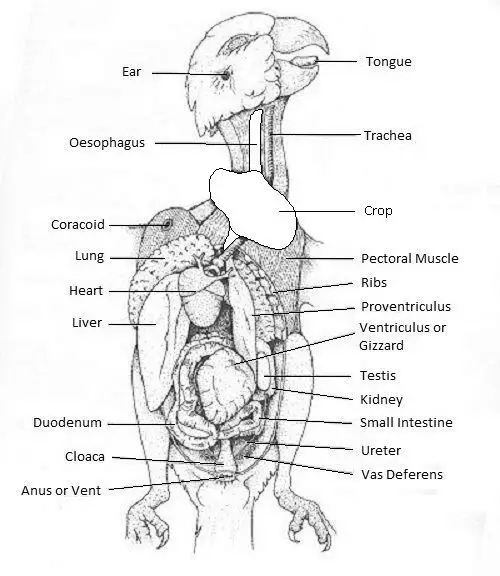
Below we will discuss budgie liver anatomy or the anatomical features of the budgie liver.
- Two Lobes
The budgie liver is split into two parts, including the right and left lobes. These lobes are separated from each other by a deep fissure. However, the right lobe is slightly bigger than the left one and lies ventrally and caudal to the heart. This is because budgies lack a diaphragm.
- Attachments
Two bile ducts enter the digestive tract, one from each lobe of the liver. However, the bile duct from the right lobe usually connects to the gallbladder.
- Covered by a Thin Membrane
Budgie’s liver is covered with a thin and fibrous membrane, the capsule. This capsule comprises many small units called hepatic lobules. Further, the lobules are made up of functional cells of the liver known as hepatocytes. Hepatocytes occupy nearly 80% of the entire liver volume and hence are responsible for performing various liver functions.
- Liver Lobules
Each lobule is made up of a central vein. Additionally, there are branches of the hepatic artery, hepatic portal vein, and bile ducts running along the corners of each lobule.
The artery transports oxygenated blood to the liver. Meanwhile, the portal vein transports deoxygenated blood containing toxins, drugs, and nutrients from the digestive tract to the liver.
The Role of the Liver in the Budgie’s Body

Budgie’s liver is involved in many essential functions. These functions include the following:
- Nutrients Metabolism
Budgie’s liver metabolizes various nutrients, including fats, carbohydrates, proteins, vitamins, and minerals. Simply, it breaks down these nutrients for ease of absorption by the bird’s body.
- Removes Toxins
Through the Hepatic portal vein, the liver removes toxins from the bird’s body’s blood supply. It then breaks down the toxins into less harmful compounds before excreting them from the body.
- Produces Bile
The liver also produces bile in the hepatocytes. Bile is critical in emulsifying dietary fats for ease of digestion and absorption.
- Regulates Blood Sugar
The liver and the pancreas help maintain a constant concentration of blood glucose. When the glucose concentrations rise, the liver immediately converts the glucose to glycogen and triglycerides. And when the glucose concentrations drop, the liver converts glycogen to glucose and releases it into the bloodstream.
- Improves Immune System
The liver is also made up of Kupffer cells. These cells can eliminate approximately 95% of pathogens that enter the budgie’s body through the blood. The cells also destroy aged blood cells, helping improve the bird’s immune system.
2. Symptoms of Budgie Liver Disease
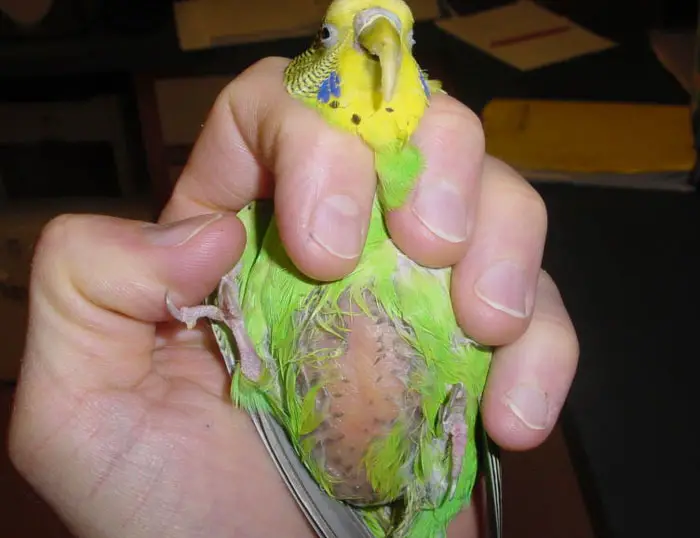

Budgie liver disease is usually slow but progressive. You can tell whether or not your bird has the disease by looking out for the following symptoms:
- Diarrhea
Liver disease in budgies may lead to digestive tract inflammation, including the lining of the intestines. Over time, the inflammation may cause increased mucus production in the intestine, leading to diarrhea.
- Difficulty Breathing
Liver disease is caused by a viral or bacterial infection. The infection may cause inflammation in the airways, making it difficult for your bird.
- Change in Droppings
Besides the droppings being watery, the color of the urates may change from white to green.
- Lethargy
Your bird may also appear inactive, weak, and tired. This may occur due to decreased appetite, accumulation of toxins in your bird’s body, and diarrhea.
Behavior Changes Associated with Liver Disease

Budgies with acute or chronic liver disease may exhibit several behavior changes. These include:
- Inactivity
Due to being weak and tired, your bird may become less active. It may also sleep longer hours than usual.
- Appetite Loss
The disease may also cause your bird to eat less than usual or stop eating entirely. This happens when the liver cannot produce bile, which is critical for digestion.
- Irritability
Chronic liver failure may cause a lot of discomfort and pain in the budgies. Consequently, your bird may become overly aggressive and irritable, especially when handled.
- Coordination Problems/Dizziness
When the liver is unable to regulate blood sugar, your budgie may experience dizziness due to low blood sugar.
Physical Changes Associated with Liver Disease

Apart from the behavioral changes, budgies with liver disease also experience various physical changes. These are:
- Weight Loss
If your bird suffers from diarrhea and loss of appetite due to liver disease, this could lead to weight loss.
- Feather Loss
Your bird may suffer from nutrient deficiency. This occurs when the liver is unable to break down all the nutrients for ease of absorption. As a result, your budgie’s feathers may become brittle and break easily, leading to feather loss. In some cases, the bird may pluck its feathers.
- Jaundice
Budgies with this disease may develop a yellowish discoloration of both in the eyes and the skin called jaundice. Budgie jaundice is caused by hyperbilirubinemia or increased excretion of biliverdin, a bile pigment in budgies.
- Bruising
Additionally, you may notice bruising around the toes and beaks of your budgies. This happens due to poor blood clotting since the liver plays a critical role in the clotting process.
- Swollen Abdomen
Liver disease may cause the build-up of fluids in the abdomen called ascites. Thus, this causes the abdomen to swell.
- Change in Feathers Color
The feathers may also change color from green to dull yellow. This happens when the bird’s liver is unable to metabolize the pigments responsible for the feather’s color.
3. Causes of Budgie Liver Disease

Also known as budgie fatty liver disease or hepatic lipidosis, this disease can have several causes, including:
- Poor Nutrition
Feeding your budgie a diet high in fat and low in protein may contribute to this disease. Such a diet may include too many sunflower seeds and nuts. Over time, the healthy liver cells may get replaced by fatty cells, causing liver damage.
Additionally, feeding your bird a diet deficient in essential nutrients may cause liver problems due to malnutrition. Consequently, this leads to liver enzyme imbalances and liver damage.
- Infections
Budgie liver failure can sometimes be due to parasitic, viral, or bacterial infections. Parasitic infections like trichomoniasis caused by parasites like protozoa and trematodes can cause liver damage.
Viral infections like avian polyomavirus disease in budgies affect many body organs, including the liver. It is contracted from the air, infected droppings, feather dust, or from infected birds. The disease usually causes liver inflammation and damage.
Besides, budgies may contract bacterial infections like chlamydiosis or psittacosis, and salmonellosis. In most cases, these infections cause liver inflammation.
- Toxic Substances
Exposure to certain toxic substances like pesticides, drugs, and heavy metals may cause liver toxicity in budgies. This may eventually lead to liver damage. Some of the metals responsible for liver toxicity are copper, lead, and zinc.
Predisposing Factors of Liver Disease in Budgies

Several factors put budgies at risk of developing liver disease. They include:
- Age
As budgies age, their liver function may decline, making them more susceptible to various liver-related diseases. Also, aging and younger birds may suffer from a weakened immune system. Hence, this usually increases their risk of infections which lead to liver damage.
- Weight
Generally, overweight birds are at a greater risk of developing fatty liver problems or hepatic lipidosis. This is because the excess fat is usually stored around the liver, impairing its function.
- Genetics
Some birds may have genetic mutations that affect how their bodies process nutrients or toxins. Accordingly, this leads to their increased risk of fatty liver illness.
Additionally, some budgies are more prone to developing budgie liver cancer because of genes. Liver cancer results from mutations to the DNA of the bird, which alters the normal function of the cells. This causes liver cells to multiply, amassing into tumors.
4. Diagnosis of Budgie Liver Disease

A physical examination is not sufficient to determine if your bird has fatty liver disease. So, here are different liver disease diagnosis methods.
- Blood Tests
Blood tests involve measuring the levels of your budgie’s liver enzymes, bile acid, and biliverdin in the blood. If the tests prove there are elevated levels of any of these compounds, it could mean your bird’s liver is damaged.
Also, serology tests exist for diagnosing liver diseases in budgies caused by viral infections. The tests demand examining blood samples for the existence of antibodies.
- Imaging
Imaging tests like MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging), X-rays (radiographs), and CT (Computed Tomography) scans can help detect liver abnormalities. These tests can detect any abscesses and tumors in the liver.
- Liver Biopsy
A liver biopsy is a test where a small sample of the liver tissue is obtained. The tissue is then probed under a microscope. During the examination, the vet may notice signs of cancer, infection, or inflammation in the liver.
Importance of Early Diagnosis
Liver disease usually progresses very quickly in budgies. If detected while still in the acute stage, this may improve the chances of your bird’s recovery. Also, it may help prevent further liver complications, which could lead to liver cancer or total failure.
Another benefit of early diagnosis is that it helps in identifying the exact liver disease causes. Consequently, this helps guide treatment methods. For example, if the disease is due to a viral infection, an effective treatment would be to use antibiotics.
5. Treatment Options for Budgie Liver Disease

Once your budgie has been diagnosed with liver disease, the next step is to start with treatment. This is how it is done.
- Medication
The common liver disease treatment is medication. Your budgie can be prescribed medicine for reducing inflammation in the liver or treating infections.
However, the correct medication for your bird depends on the specific cause of the disease. For example, if the cause is an infection, your budgie may be prescribed antibiotics along with pain medication.
- Dietary Changes
Another treatment option is making changes to your budgie’s diet. The changes include giving your bird a balanced diet comprising 60%-80% pellets supplemented with fruits, vegetables, and seed mixes. Also, the diet should be low in fat.
- Supportive Care
This involves implementing measures that help your sick budgie feel more comfortable for quick recovery. Such measures may include regularly keeping the cage clean and adding supplements into their diet, like vitamin E.
Just ensure to consult an avian medicine expert before giving your birds any supplements. These experts are more knowledgeable about avian medication and have vast experience in offering management strategies for avian diseases. More so, they are certified to practice their profession.
Supportive care also includes assisted feeding and fluid therapy to help maintain your bird’s electrolyte balance.
Long-Term Management Strategies for Liver Disease in Budgies
The best management strategies for liver disease in birds like the budgie depend on the cause and severity of the illness. Here are some general strategies:

- Regular Veterinary Care
Regular check-ups are critical in monitoring the function of your bird’s liver. Through the check-ups, the vet can identify any concerns with the liver early on and adjust the treatment if it’s necessary.
- Exercises
You should not let your budgie stay in the cage all day. Instead, you should offer opportunities for exercise and mental stimulation. Keeping your bird engaged will prevent your bird from becoming obese.
- Minimize Exposure to Toxins
Once your budgie is back from the vet clinic, you should limit its exposure to toxins in the house. These include cigarette smoke and fumes from cleaning products. This will help prevent further damage to the liver and ensure a speedy recovery.
6. Preventing Budgie Liver Disease

Several preventive measures may help reduce the risk of your budgie developing liver disease. These include:
- Weight Management
Proper bird nutrition is critical in managing your pet’s weight. So, you should avoid giving your budgie treats high in fat or sugar content, like nuts and sunflower seeds, frequently. Also, don’t let your bird eat foods like chocolate, dairy products, and cheese.
- Always Keep the Cage Clean
A dirty cage can encourage the growth of harmful bacteria, leading to infections. These bacterial infections may lead to liver damage.
- Offer Clean Water
Always ensure your bird has access to fresh water all the time for optimal liver health.
- Avoid Toxic Substances
Ensure your bird’s environment is clean and toxin-free. This will help prevent liver toxicity, which could lead to liver disease.
Importance of Proper Nutrition and Hygiene
Proper nutrition and hygiene can help prevent a wide range of budgie health problems, including liver disease. This is because a diet that lacks all the essential nutrients may lead to malnutrition and weakened immune function. Consequently, it may make your budgie more susceptible to viral and bacterial infections.

On the other hand, good hygiene practices like keeping the cage clean may help prevent the spread of diseases between the budgies. Also, a clean cage can prevent the growth of bacteria-causing infections.
Conclusion
Studying the anatomy of the budgie liver can help you understand better the different roles of this organ. You also get to understand more about liver disease in these birds, including its symptoms, causes, diagnosis, treatment, and preventive measures.
Having said that, there are several implications to understanding avian liver disease or avian hepatology for pet care. For example, it guarantees early detection when you are familiar with the disease’s symptoms, allowing successful treatment.
Also, it ensures you have knowledge about the risk factors of this disease, enabling you to take steps to prevent it. More importantly, you get to learn the various ways to promote the overall health of the liver.
Worth mentioning is that more avian liver disease research is needed as this disease is common among birds. And the research should focus more on identifying more treatment options and improved diagnostic techniques for this disease.







